Building Envelope Enhancements That Save Energy sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with casual formal language style and brimming with originality from the outset.
The discussion delves into the key components, benefits, technologies, and sustainable practices related to enhancing building envelopes for energy efficiency.
Building Envelope Components
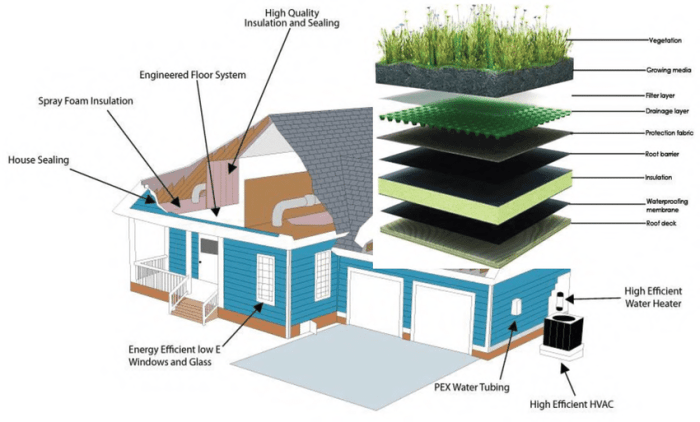
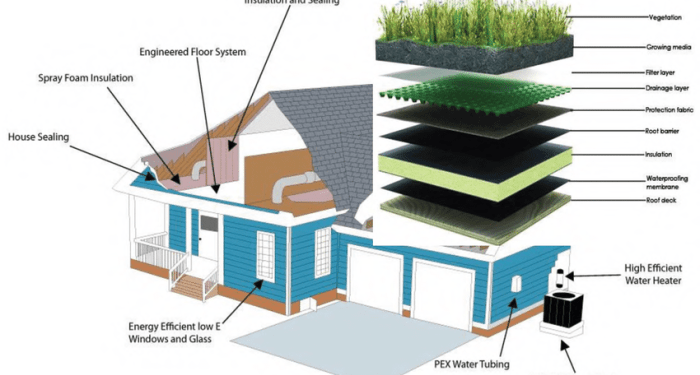
The building envelope is the physical separator between the interior and exterior environments of a building. It includes the walls, roof, foundation, windows, and doors, all working together to provide protection and energy efficiency.The key elements of a building envelope and their contributions to energy efficiency are as follows:
Walls
Walls are crucial components of the building envelope, providing insulation and structural support. Materials commonly used in wall construction include concrete, wood, brick, and insulation materials like fiberglass or foam. Proper insulation in walls helps regulate indoor temperature and reduces the need for heating and cooling, thus saving energy.
Roof
The roof plays a significant role in energy efficiency by providing protection from the elements and helping to maintain a consistent indoor temperature. Common roofing materials include shingles, metal, tiles, and green roofs. Proper insulation and reflective roofing materials can reduce heat gain in the summer and heat loss in the winter, leading to energy savings.
Windows and Doors
Windows and doors are essential components of the building envelope that allow natural light and ventilation while providing security and insulation. Materials commonly used for windows and doors include glass, wood, aluminum, and vinyl. Energy-efficient windows with double or triple glazing, low-emissivity coatings, and insulated frames help minimize heat transfer, improving overall energy efficiency.Overall, each component of the building envelope plays a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency and reducing energy consumption in buildings.
Benefits of Enhancing Building Envelopes
Improving the building envelope offers a range of benefits, particularly in terms of energy savings and overall building performance. By upgrading the envelope, building owners can significantly reduce energy consumption, leading to cost savings and environmental benefits.
Enhanced Insulation
Upgrading the insulation in a building envelope can greatly reduce heat transfer, helping to maintain a consistent indoor temperature. This leads to lower heating and cooling costs throughout the year, resulting in significant energy savings.
Air Tightness
Enhancing the air tightness of a building envelope prevents drafts and air leakage, which can account for a significant portion of energy loss in a building. By sealing air leaks, building owners can lower their energy consumption and improve the overall comfort of the indoor environment.
Case Studies
Numerous case studies have demonstrated the energy-saving potential of enhancing building envelopes. For example, a commercial building in a cold climate saw a 20% reduction in heating costs after upgrading its insulation and air sealing. Similarly, a residential building in a hot climate experienced a 15% decrease in cooling costs following envelope enhancements.
Financial Benefits
In addition to energy savings, improving the building envelope can also increase the value of the property and attract potential buyers or tenants. Building owners can recoup their initial investment through reduced energy bills and improved building performance, making envelope enhancements a worthwhile long-term investment.
Technologies for Enhancing Building Envelopes
Enhancing building envelopes involves the use of innovative technologies to improve energy efficiency and reduce heat loss or gain. These technologies play a crucial role in creating sustainable and comfortable indoor environments while lowering energy costs.
Smart Technologies for Energy Efficiency
Smart technologies such as sensors, controls, and automation systems are being integrated into building envelopes to optimize energy usage. These technologies can monitor and adjust heating, cooling, and lighting systems based on real-time data, ensuring efficient operation and reducing energy waste.
Insulation for Thermal Performance
- Proper insulation materials like fiberglass, foam, or cellulose are essential for enhancing the thermal performance of building envelopes. Insulation helps to minimize heat transfer through walls, roofs, and floors, reducing the need for heating or cooling systems.
- Advanced insulation techniques, such as spray foam or aerogel insulation, provide superior thermal resistance and can significantly improve energy efficiency in buildings.
High-Performance Windows and Doors
- Energy-efficient windows and doors with low-emissivity coatings, multiple glazing layers, and insulated frames help to minimize heat transfer and air leakage. These high-performance components enhance the overall energy efficiency of building envelopes.
- Smart windows with dynamic glazing technology can automatically adjust tint levels based on external conditions, reducing solar heat gain and glare while maximizing natural light penetration.
Air Sealing and Ventilation Systems
- Proper air sealing techniques, such as weather-stripping, caulking, and sealing penetrations, prevent air leaks and drafts in building envelopes. This helps to maintain consistent indoor temperatures and reduce the workload on heating and cooling systems.
- Energy recovery ventilation systems can improve indoor air quality while recovering heat or coolness from outgoing air streams, further enhancing energy efficiency in buildings.
Sustainable Practices in Building Envelope Design
When it comes to building envelope design, incorporating sustainable practices is essential for reducing environmental impact and improving energy efficiency. Sustainable design focuses on using eco-friendly materials and implementing practices that minimize waste and energy consumption throughout the lifecycle of a building.
Eco-Friendly Materials and Practices
One of the key aspects of sustainable building envelope design is the use of eco-friendly materials. Examples of such materials include:
- Bamboo: A rapidly renewable resource that can be used for flooring, siding, and other structural elements.
- Recycled Glass: Used in windows and cladding to reduce the demand for new materials.
- Sustainable Insulation: Made from recycled materials or natural fibers like wool or cotton.
Importance of Sustainability in Modern Construction
Sustainability is crucial in modern construction due to its numerous benefits, such as:
- Energy Efficiency: Sustainable building envelopes can help reduce energy consumption for heating, cooling, and lighting, leading to lower utility costs.
- Environmental Impact: By using eco-friendly materials and practices, construction projects can minimize waste and greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a healthier planet.
- Health and Well-being: Sustainable buildings often provide better indoor air quality and thermal comfort, creating healthier living and working environments for occupants.
Closure
In conclusion, Building Envelope Enhancements That Save Energy present a compelling case for the significant impact of envelope upgrades on energy conservation, sustainability, and overall building performance. Dive into this transformative journey towards energy-efficient structures today.
Common Queries
What are some common materials used in building envelopes??
Materials commonly used in building envelopes include concrete, steel, glass, wood, and insulation materials like fiberglass or foam boards.
How do smart technologies improve energy efficiency in building envelopes?
Smart technologies like sensors, automated controls, and energy management systems help monitor and optimize energy usage, heating, and cooling within a building, leading to improved efficiency.
Why is sustainability important in modern construction?
Sustainability in modern construction ensures that buildings are designed, built, and operated in an environmentally friendly manner, reducing energy consumption, waste generation, and overall environmental impact.